December 1, 2020
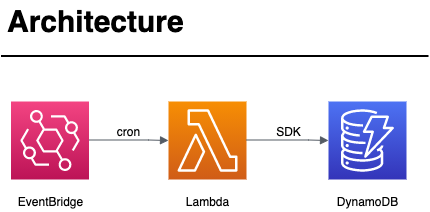
Objective
Write an AWS Lambda that manually scales a global DynamoDB table
Why?
DynamoDB tables can be set to automatically scale based on load. However, this process can take quite a while. We needed to scale up at a precise time to be ready for large batch loads.
According to the auto scaling guide, DynamoDB auto scaling modifies provisioned throughput settings only when the actual workload stays elevated (or depressed) for a sustained period of several minutes. If you have a batch load that will greatly increase load on the system with no ramp-up time, this will cause early slowdowns. If you have sudden, short-duration spikes of activity, consult the burst capacity guide. If you can wait several minutes for ramp-up, auto-scaling should work fine for your use case.
MVP
Scale a single (non-global) table
- Turn off auto-scaling for the table (Provisioned)
- Use the DynamoDB SDK v1
- Explicitly call the SDK to set the Read Capacity Units (RCU) and Write Capacity Units (WCU) on the table
- Initialize configuration
private ClientConfiguration clientConfiguration() {
final ClientConfiguration clientConfiguration = new ClientConfiguration();
// These constants are typically environment variables specific to your environment
// Note: proxy host and port are required in SDK v1
clientConfiguration.setProxyHost(AWS_PROXY_HOST);
clientConfiguration.setProxyPort(Integer.valueOf(AWS_PROXY_PORT));
clientConfiguration.setClientExecutionTimeout(CLIENT_TIMEOUT);
clientConfiguration.setProtocol(Protocol.HTTP);
return clientConfiguration;
}
private AmazonDynamoDB getClient() {
// SDK v1 uses the AmazonDynamoDBClientBuilder (v2 does not)
return AmazonDynamoDBClientBuilder.standard()
.withClientConfiguration(clientConfiguration())
.withRegion(Regions.valueOf(REGION))
.build();
}
- Call the SDK
// The RCU/WCU can be set directly in this case
ProvisionedThroughput table_throughput = new ProvisionedThroughput(
read_capacity, write_capacity);
try {
// Update the DynamoDB table with the ProvisionedThroughput
getClient().updateTable(table_name, table_throughput);
} catch (AmazonServiceException e) {
System.err.println(e.getErrorMessage());
System.exit(1);
}
Full Version
Scale a global table
- In this example, the primary table is in us-east-1. A global table was created with a replica in us-west-2
- Global tables must use auto-scaling
- Setting the RCU/WCU explicitly on an auto-scaled table does not actually change the RCU/WCU (approach for MVP will not work)
- Upgrade to SDK v2 to simplify setting the auto-scaling parameters (Note: SDK v2 is quite different from v1 but has simplified the API for DynamoDB manipulation)
- Set the minimum RCU/WCU on the auto-scaler instead
- Initialize client
private DynamoDbClient getClient() {
// These constants are typically environment variables specific to your environment
ApacheHttpClient.Builder httpClientBuilder = ApacheHttpClient.builder()
.connectionTimeout(CONNECTION_TIMEOUT)
.socketTimeout(SOCKET_TIMEOUT);
RetryPolicy.Builder retryBuilder = RetryPolicy.builder()
.numRetries(RETRY_LIMIT);
ClientOverrideConfiguration.Builder clientOverrideBuilder =
ClientOverrideConfiguration.builder()
.apiCallAttemptTimeout(API_CALL_ATTEMPT_TIMEOUT)
.apiCallTimeout(API_CALL_TIMEOUT)
.retryPolicy(retryBuilder.build());
// New DynamoDbClient.builder() for SDK v2
return DynamoDbClient.builder()
.httpClientBuilder(httpClientBuilder)
.overrideConfiguration(clientOverrideBuilder.build())
.build();
}
- Call the SDK
// A series of updates are required to change the auto scaling settings
AutoScalingTargetTrackingScalingPolicyConfigurationUpdate policyConfigurationUpdate =
AutoScalingTargetTrackingScalingPolicyConfigurationUpdate.builder()
.targetValue(SCALING_POLICY_TARGET_VALUE)
.build();
AutoScalingPolicyUpdate policyUpdate = AutoScalingPolicyUpdate.builder()
.targetTrackingScalingPolicyConfiguration(policyConfigurationUpdate)
.build();
// The maximum auto scale capacity is not really used here and can be set to an arbitrarily high number
AutoScalingSettingsUpdate.Builder updateBuilder = AutoScalingSettingsUpdate.builder()
.maximumUnits(MAX_AUTOSCALE_CAPACITY)
.scalingPolicyUpdate(policyUpdate);
// The minimum units are changed to force a manual scale up/down
AutoScalingSettingsUpdate rcuUpdate = updateBuilder.minimumUnits(HIGH_READ_CAPACITY_UNITS).build();
AutoScalingSettingsUpdate wcuUpdate = updateBuilder.minimumUnits(HIGH_WRITE_CAPACITY_UNITS).build();
// The read capacity units must be updated for each replica
ReplicaAutoScalingUpdate eastReplicaUpdate = ReplicaAutoScalingUpdate.builder()
.regionName("us-east-1")
.replicaProvisionedReadCapacityAutoScalingUpdate(rcuUpdate)
.build();
ReplicaAutoScalingUpdate westReplicaUpdate = ReplicaAutoScalingUpdate.builder()
.regionName("us-west-2")
.replicaProvisionedReadCapacityAutoScalingUpdate(rcuUpdate)
.build();
// The write capacity units impact all replicas
UpdateTableReplicaAutoScalingRequest autoScalingRequest = UpdateTableReplicaAutoScalingRequest.builder()
.tableName(TABLE_NAME)
.replicaUpdates(eastReplicaUpdate, westReplicaUpdate)
.provisionedWriteCapacityAutoScalingUpdate(wcuUpdate)
.build();
try {
getClient().updateTableReplicaAutoScaling(autoScalingRequest);
} catch (AmazonServiceException e) {
System.err.println(e.getErrorMessage());
System.exit(1);
}
Issues
The code above worked great until the Lambda was deployed in us-west-2 for redundancy. The SDK calls from us-west-2 were timing out.
- For testing purposes, no SDK v2 calls worked but v1 calls did
- The solution is to initialize the SDK v1 and then make the SDK v2 calls
- Add a call to
getTable(TABLE_NAME)from the SDK v1 before the call toupdateTableReplicaAutoScaling - Note: SDK v1 needs the proxy specified but SDK v2 does not
- Timeouts for the SDK v2 calls may need to be increased from us-west-2
Disclaimer
These issues may have been specific to my particular environment. If you experience similar issues, this should help you resolve them. If you have found a solution to the us-west-2 problem, please reach out!






Comments